Alibaba doubles down on RISC-V architecture with a new secretive 'server-grade' chip that will put AMD and Intel on alert - Related to get, ai, team, that's, copilot
Alibaba doubles down on RISC-V architecture with a new secretive 'server-grade' chip that will put AMD and Intel on alert

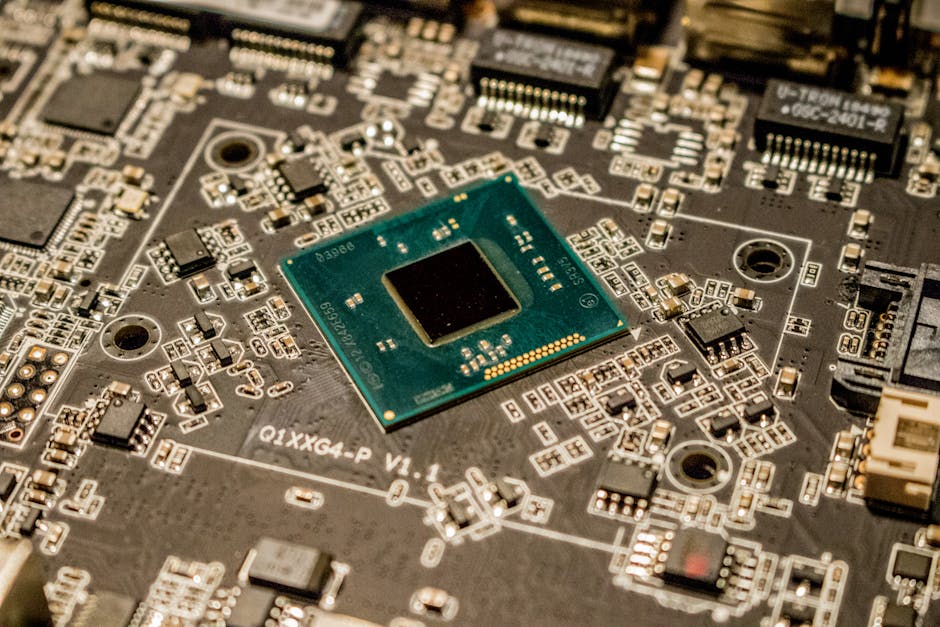
Alibaba's DAMO Academy has launched its first server-grade RISC-V processor.
The C930 is designed for high-performance computing, rivaling Intel and AMD's offerings.
RISC-V's open-source design avoids licensing fees and geopolitical restrictions.
Alibaba has launched its first server-grade RISC-V processor, the C930, designed for high-performance computing and positioned as an alternative to Intel Xeon and AMD EPYC CPUs.
The new chip, developed by Alibaba’s research arm DAMO Academy (short for Discovery, Adventure, Momentum and Outlook), was revealed at a conference in Beijing and is the latest addition to Alibaba’s XuanTie RISC-V processor series, which includes the C910 launched in 2019 and the C920 released in 2023.
In response to the ever-tightening US trade restrictions on advanced technology exports, Chinese firms such as Alibaba’s DAMO Academy, Huawei, and Tencent have been ramping up efforts to develop their own chips to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers. RISC-V in particular is gaining traction in China due to its open source nature, which allows companies to design and customize processors without the licensing fees or geopolitical risks associated with proprietary architectures like x86 and Arm. The Chinese Academy of Sciences is set to introduce its own RISC-V-based XiangShan CPU this year.
At the Beijing conference, DAMO Academy also outlined future plans for the XuanTie processor series, which includes the development of new chips for use in AI accelerators, automotive computing, and high-speed interconnection.
A analysis from the South China Morning Post, which is owned by Alibaba, states, “The launch of the new chips came days after the tech giant unveiled an aggressive investment plan of at least 380 billion yuan (US$52 billion) in AI and cloud infrastructure over the next three years. The organization, which is China’s largest cloud provider, aims to meet surging demand for AI models fuelled by the recent popularity of the high-performance, low-cost models developed by Hangzhou-based start-up DeepSeek.”.
The reports adds the planned outlay exceeds Alibaba’s total spending on AI infrastructure over the past decade and will lead to the construction of more data centers across China.
The new C930 server processor is expected to begin shipping to clients later in March 2025.
When you purchase through StackSocial links in our articles, we may earn a small commission. This doesn’t affect our editorial independence.
AMD Radeon RX 9070 (XT): Wie gefallen euch die neuen Grafikkarten und kauft ihr eine?
Haben RDNA 4 und FSR 4 euch positiv überraschen können, hat AMD......
Microsoft nutzt bei den KI-Assistenten Copilot derzeit die Modelle von OpenAI als technisches Grundgerüst. Wie Reuters unter Berufung auf The Informat......
Copilot might soon get more Microsoft AI models, less ChatGPT presence

Table of Contents Table of Contents Steadily building its own stack Rivalry, and openness to rivals.
Microsoft is one of the early backers of OpenAI, and has repeatedly hawked products like Copilot by touting their access to the latest ChatGPT models. Now, it seems Microsoft is looking to push its own AI models in the popular software suite, while also developing a rival to OpenAI’s reasoning models in the ”GPT-o” family.
As per The Information, employees at Microsoft’s AI unit not long ago concluded the training of “a new family of AI model” that are currently in development under the “MAI” codename. Internally, the team is hopeful that these in-house models perform nearly as well as the top AI models from the likes of OpenAI and Anthropic.
Under the leadership of its AI chief, Mustafa Suleyman, Microsoft is launching this initiative to trim down its dependence on OpenAI and develop its own AI stack for Copilot applications. The developments are not surprising.
In the last week of February, Microsoft introduced new small language models called Phi-4-multimodal and Phi-4-mini. They come with multi-modal capabilities, which means they can process text, speech, and vision as input formats, just like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini.
These two new AI models are already available to developers via Microsoft’s Azure AI Foundry and third-party platforms such as HuggingFace and the NVIDIA API Catalog. In benchmarks shared by the enterprise, the Phi-4 model is already ahead of Google’s latest Gemini [website] series models on multiple test parameters.
“It is among a few open models to successfully implement speech summarization and achieve performance levels comparable to GPT-4o model,” Microsoft noted in its blog post. The enterprise is hoping to release its ”MAI” models commercially via its Azure service.
Aside from testing in-house AI models for Copilot, Microsoft is also exploring third-party options such as DeepSeek, xAI, and Meta. DeepSeek in the recent past made waves by offering a high performance benchmark at a dramatically lower development cost. It has already been adopted by numerous companies and in the recent past claimed a theoretical cost-to-profit ratio of over 500% on a daily basis.
Today, we are advancing our AI ambitions with the release of DeepSeek R1 7B & 14B distilled models for Copilot+ PCs via Azure AI Foundry. This is the next step on our journey to continue to make Windows the platform for AI, seamlessly integrating intelligence from the cloud to… [website] — Pavan Davuluri (@pavandavuluri) March 3, 2025.
Aside from developing its own AI models to replace OpenAI’s GPT infrastructure for Copilot, Microsoft is also reportedly working on its own reasoning AI models, too. This would pit Microsoft against OpenAI products such as GPT-o1 as well as Chinese upstarts such as DeepSeek, both of which offer reasoning capabilities.
Apparently, the work on an in-house reasoning model has been expedited due to strained relationships between Microsoft and OpenAI teams over technology sharing. , Suleyman and OpenAI have been at odds over the latter’s lack of transparency regarding the intricate workings of its AI models such as GPT-o1.
Reasoning models are deemed to be the next frontier for AI development, as they offer a more nuanced understanding of queries, logical deduction, and superior problem solving capabilities. Microsoft also indicates that its Phi-4 model delivers stronger language, mathematical, and visual science reasoning chops.
Something to look forward to: AMD has confirmed the pricing and launch date for its latest high-performance processors, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D and Ryzen ......
Dynabook Portégé Z40L-N offers customizable configurations and extended warranties.
Microsoft Secured-core PC integrates chip-to-cloud security for bu......
Gemini, Google's AI chatbot running the [website] Flash model, is well equipped to handle complex conversations, generate instant images (.
Well, that's unexpected: Samsung will team up with its fiercest Chinese rival to produce next gen NAND flash

Samsung has signed an agreement with China’s YMTC to use its hybrid bonding tech.
The move will prevent infringement asserts in production of 400-layer NAND.
US-China trade tensions may also have influenced the agreement.
Samsung Electronics has signed a contract with Yangtze Memory Technologies Co. (YMTC) which will allow it to use the Chinese semiconductor corporation’s bonding technology in the production of its 400-layer NAND flash memory.
Founded in 2016 and headquartered in Wuhan, China, YMTC is a subsidiary of Tsinghua Unigroup, which is backed by the Chinese government. It focuses on 3D NAND flash memory, a critical component in storage devices like SSDs, smartphones, and data centers, and most famously developed Xtacking technology, a proprietary architecture that improves NAND flash performance and density.
’s ChosunBiz news site, Samsung likely entered into the agreement to avoid a patent dispute related to this “hybrid bonding,” which will be an essential process in the mass production of 400-layer NAND memory.
"YMTC registered the hybrid bonding patent and was the first to apply the relevant technology in the manufacturing process of NAND flash memory. Although YMTC significantly trails behind global memory semiconductor corporations such as Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix in terms of market share, it is quickly catching up with South Korean firms, lately starting mass production of 294-layer NAND flash memory," the site explains.
It is believed the agreement will protect both firms from violating each other’s patents. YMTC sued Micron in a [website] court last year, alleging infringement of its NAND tech.
ChosunBiz quotes a semiconductor industry insider as saying, “In the memory semiconductor industry, companies sign licensing agreements in advance to avoid patent disputes ahead of next-generation product development and manufacturing. While such agreements are a common practice in the industry, concerns are growing over the rapid narrowing of the technology gap between China and leading companies, as Samsung, the top player in the NAND flash memory market, is now using patents from a Chinese firm.”.
eeNews Analog points out that there could be more to the agreement than just wanting to avoid infringement. “It may also reflect that a US-China trade war may impact YMTC’s ability to sell memory components outside China and that a licensing or cross-licensing arrangement for various technologies could benefit YMTC,” the site writes.
ChosunBiz’s article doesn’t mention SK Hynix, Samsung’s South Korean memory rival, but it’s possible - likely even - that it too will have explored or entered into similar licensing agreements with YMTC to secure the hybrid bonding technology for its own NAND flash production.
Earlier in the week, online chatter pointed to a possible delay in the production of Panther Lake silicon. Well-known industry analyst—Ming-Chi Kuo—ha......
Gemini, Google's AI chatbot running the [website] Flash model, is well equipped to handle complex conversations, generate instant images (.
Looking for a different day? A new Quordle puzzle appears at midnight each day for your time zone – which means that some people are always playing 't......
Market Impact Analysis
Market Growth Trend
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.9% | 5.9% | 6.2% | 6.9% | 7.3% | 7.5% | 7.6% |
Quarterly Growth Rate
| Q1 2024 | Q2 2024 | Q3 2024 | Q4 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6.9% | 7.2% | 7.4% | 7.6% |
Market Segments and Growth Drivers
| Segment | Market Share | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors | 35% | 9.3% |
| Consumer Electronics | 29% | 6.2% |
| Enterprise Hardware | 22% | 5.8% |
| Networking Equipment | 9% | 7.9% |
| Other Hardware | 5% | 5.3% |
Technology Maturity Curve
Different technologies within the ecosystem are at varying stages of maturity:
Competitive Landscape Analysis
| Company | Market Share |
|---|---|
| Apple | 18.7% |
| Samsung | 16.4% |
| Intel | 12.9% |
| NVIDIA | 9.8% |
| AMD | 7.3% |
Future Outlook and Predictions
The That Will Alibaba landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, changing threat vectors, and shifting business requirements. Based on current trends and expert analyses, we can anticipate several significant developments across different time horizons:
Year-by-Year Technology Evolution
Based on current trajectory and expert analyses, we can project the following development timeline:
Technology Maturity Curve
Different technologies within the ecosystem are at varying stages of maturity, influencing adoption timelines and investment priorities:
Innovation Trigger
- Generative AI for specialized domains
- Blockchain for supply chain verification
Peak of Inflated Expectations
- Digital twins for business processes
- Quantum-resistant cryptography
Trough of Disillusionment
- Consumer AR/VR applications
- General-purpose blockchain
Slope of Enlightenment
- AI-driven analytics
- Edge computing
Plateau of Productivity
- Cloud infrastructure
- Mobile applications
Technology Evolution Timeline
- Technology adoption accelerating across industries
- digital transformation initiatives becoming mainstream
- Significant transformation of business processes through advanced technologies
- new digital business models emerging
- Fundamental shifts in how technology integrates with business and society
- emergence of new technology paradigms
Expert Perspectives
Leading experts in the hardware tech sector provide diverse perspectives on how the landscape will evolve over the coming years:
"Technology transformation will continue to accelerate, creating both challenges and opportunities."
— Industry Expert
"Organizations must balance innovation with practical implementation to achieve meaningful results."
— Technology Analyst
"The most successful adopters will focus on business outcomes rather than technology for its own sake."
— Research Director
Areas of Expert Consensus
- Acceleration of Innovation: The pace of technological evolution will continue to increase
- Practical Integration: Focus will shift from proof-of-concept to operational deployment
- Human-Technology Partnership: Most effective implementations will optimize human-machine collaboration
- Regulatory Influence: Regulatory frameworks will increasingly shape technology development
Short-Term Outlook (1-2 Years)
In the immediate future, organizations will focus on implementing and optimizing currently available technologies to address pressing hardware tech challenges:
- Technology adoption accelerating across industries
- digital transformation initiatives becoming mainstream
These developments will be characterized by incremental improvements to existing frameworks rather than revolutionary changes, with emphasis on practical deployment and measurable outcomes.
Mid-Term Outlook (3-5 Years)
As technologies mature and organizations adapt, more substantial transformations will emerge in how security is approached and implemented:
- Significant transformation of business processes through advanced technologies
- new digital business models emerging
This period will see significant changes in security architecture and operational models, with increasing automation and integration between previously siloed security functions. Organizations will shift from reactive to proactive security postures.
Long-Term Outlook (5+ Years)
Looking further ahead, more fundamental shifts will reshape how cybersecurity is conceptualized and implemented across digital ecosystems:
- Fundamental shifts in how technology integrates with business and society
- emergence of new technology paradigms
These long-term developments will likely require significant technical breakthroughs, new regulatory frameworks, and evolution in how organizations approach security as a fundamental business function rather than a technical discipline.
Key Risk Factors and Uncertainties
Several critical factors could significantly impact the trajectory of hardware tech evolution:
Organizations should monitor these factors closely and develop contingency strategies to mitigate potential negative impacts on technology implementation timelines.
Alternative Future Scenarios
The evolution of technology can follow different paths depending on various factors including regulatory developments, investment trends, technological breakthroughs, and market adoption. We analyze three potential scenarios:
Optimistic Scenario
Rapid adoption of advanced technologies with significant business impact
Key Drivers: Supportive regulatory environment, significant research breakthroughs, strong market incentives, and rapid user adoption.
Probability: 25-30%
Base Case Scenario
Measured implementation with incremental improvements
Key Drivers: Balanced regulatory approach, steady technological progress, and selective implementation based on clear ROI.
Probability: 50-60%
Conservative Scenario
Technical and organizational barriers limiting effective adoption
Key Drivers: Restrictive regulations, technical limitations, implementation challenges, and risk-averse organizational cultures.
Probability: 15-20%
Scenario Comparison Matrix
| Factor | Optimistic | Base Case | Conservative |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Timeline | Accelerated | Steady | Delayed |
| Market Adoption | Widespread | Selective | Limited |
| Technology Evolution | Rapid | Progressive | Incremental |
| Regulatory Environment | Supportive | Balanced | Restrictive |
| Business Impact | Transformative | Significant | Modest |
Transformational Impact
Technology becoming increasingly embedded in all aspects of business operations. This evolution will necessitate significant changes in organizational structures, talent development, and strategic planning processes.
The convergence of multiple technological trends—including artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and ubiquitous connectivity—will create both unprecedented security challenges and innovative defensive capabilities.
Implementation Challenges
Technical complexity and organizational readiness remain key challenges. Organizations will need to develop comprehensive change management strategies to successfully navigate these transitions.
Regulatory uncertainty, particularly around emerging technologies like AI in security applications, will require flexible security architectures that can adapt to evolving compliance requirements.
Key Innovations to Watch
Artificial intelligence, distributed systems, and automation technologies leading innovation. Organizations should monitor these developments closely to maintain competitive advantages and effective security postures.
Strategic investments in research partnerships, technology pilots, and talent development will position forward-thinking organizations to leverage these innovations early in their development cycle.
Technical Glossary
Key technical terms and definitions to help understand the technologies discussed in this article.
Understanding the following technical concepts is essential for grasping the full implications of the security threats and defensive measures discussed in this article. These definitions provide context for both technical and non-technical readers.
RISC-V intermediate
CPU intermediate
RAM intermediate
API beginner
 How APIs enable communication between different software systems
How APIs enable communication between different software systems